Since 2009, the HITECH Act spurred widespread adoption of Electronic Health Records, revolutionizing healthcare by enhancing patient care and streamlining management.
EHRs empower practice managers with advanced tools that improve patient care, allowing for real-time data access and effective decision-making.
EHRs facilitate effortless data exchange within healthcare systems, promoting better coordination and communication among healthcare providers.
With the introduction of the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act in 2009, Electronic Health Records (EHRs) have become a cornerstone in modern healthcare management. This legislative milestone accelerated the digital transformation of healthcare, equipping practice managers with the tools to elevate patient care, streamline administrative tasks, and enable efficient data exchange within the healthcare ecosystem.
The transition to EHRs has been a pivotal development in healthcare, revolutionizing both patient care and operational efficiency across the industry. This guide aims to help you understand the value of implementing EHRs for simplifying administrative processes and improving patient outcomes.
Key advantages of leveraging electronic health records in your medical practice
Enhanced patient care and safety
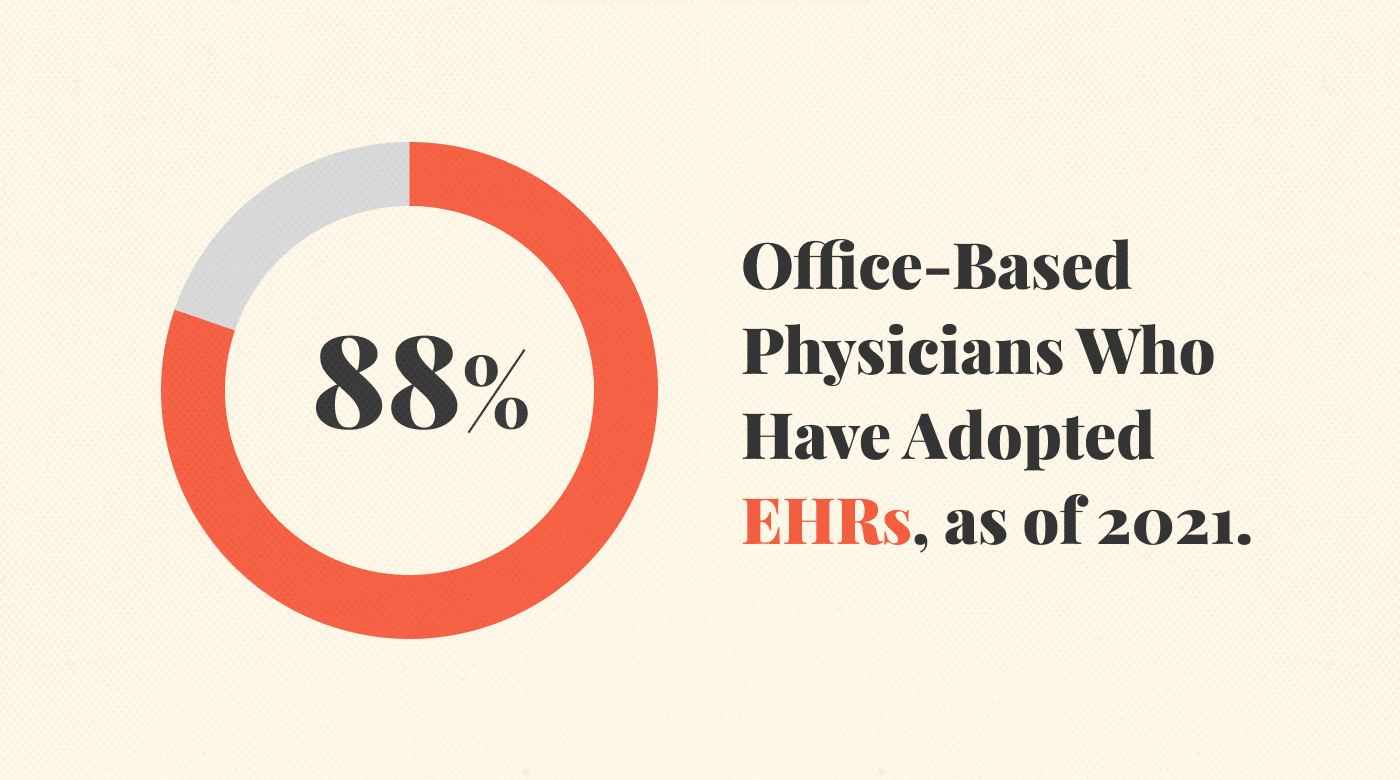
As of 2021, 78% of office-based physicians have adopted certified EHRs, underscoring their role in improving patient care, streamlining operations, and enhancing coordinated care.
Here are 3 primary ways EHRs contribute to better patient care:
Access to patient information
- EHRs offer quick, digital access to full patient histories—enabling better care.
- Secure access for authorized users ensures informed, timely treatment decisions.
Coordination and continuity of care
- EHRs enable care coordination across settings—boosting effective collaboration.
- Digital records offer a full view of patient health—aiding in treatment choices.
Patient engagement
- EHRs give patients direct access to their health data—encouraging self-management.
- HIPAA-compliant electronic communication with providers enhances patient understanding—enabling informed choices.
Integrating EHRs into healthcare practices has been proven to enhance patient care and safety, as substantiated by a review in JMIR Medical Informatics. The use of EHRs not only improves diagnostics and patient outcomes but also minimizes medical errors and treatment delays commonly associated with paper-based records. For practice managers, this makes EHR adoption a logical step in optimizing both patient care and operational efficiency.
Want to streamline your medical practice? Unlock efficiency with our curated list of the best EHR software.
Efficiency and cost savings
EHRs improve patient care and safety while also boosting efficiency and reducing costs. Research indicates that enhanced EHR functionality can cut hospital operating costs, potentially saving $78-$81 billion in annual health spending.
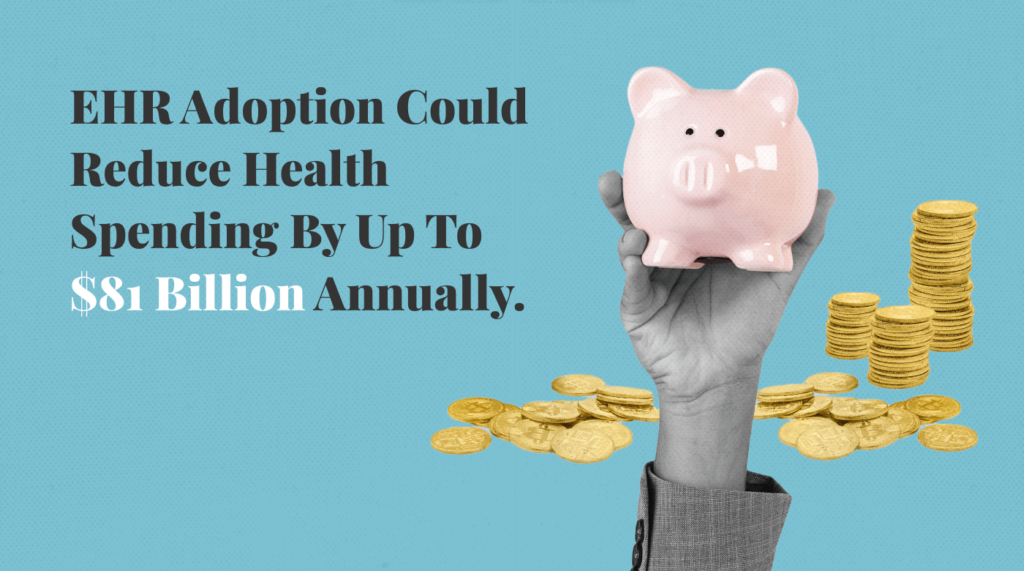
These cost savings are attributed to the efficiency gains and improved management facilitated by EHR systems. Let's take a look at exactly how EHRs drive efficiency and reduce costs below.
Time-saving benefits
- EHRs expedite documentation, freeing up time for direct patient care.
- Quick data retrieval in EHRs eliminates manual searches, saving time.
Reduced paperwork and storage costs
- EHRs eliminate extensive paperwork, reducing administrative burden.
- Reduced physical storage needs cut costs on filing and off-site facilities.
Streamlined billing and reimbursement process
- EHRs automate billing and coding, enhancing revenue cycle management.
- Integration with billing systems minimizes manual data entry and tasks.
Reduced patient admission
- EHRs identify at-risk groups, aiding in proactive chronic condition management.
- Early intervention via EHRs improves patient outcomes and cuts hospital costs.
Implementing electronic health records ultimately helps medical practices achieve their business goals. It does so by optimizing operational efficiency and reducing costs. By embracing EHR technology, healthcare providers can focus on delivering high-quality patient care while maximizing financial performance.
Clinical decision making
Electronic health records play a significant role in improving clinical decision making and driving better healthcare outcomes. EHRs empower healthcare professionals by harnessing data analytics and providing comprehensive patient information.
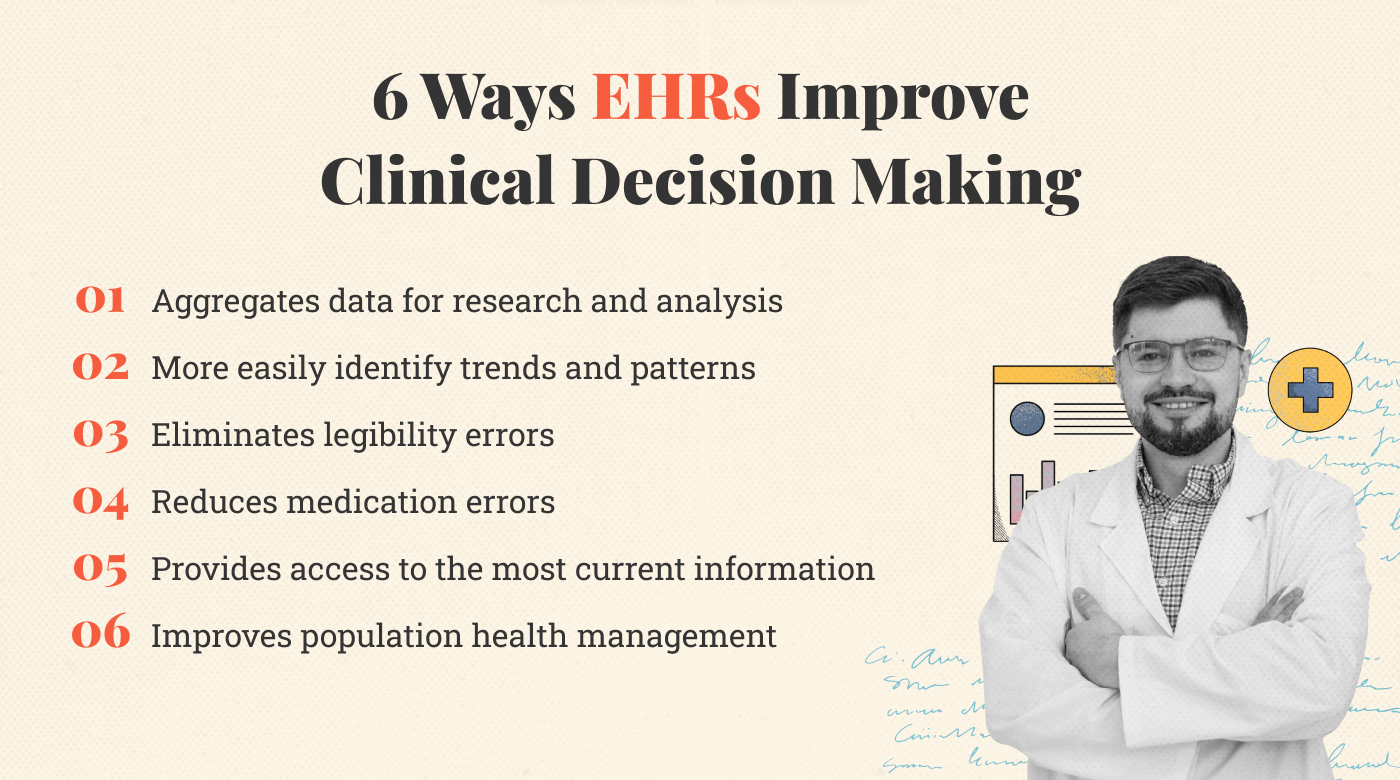
This data enables them to make informed decisions and deliver personalized care. These are the key benefits of EHRs for clinical decision making:
Improved data analysis
EHRs enable healthcare providers to leverage advanced data analysis tools to gain insights from vast amounts of patient data. This enhanced data analysis capability offers several benefits, including:
- Making informed decisions: EHRs support evidence-based decisions by analyzing multi-source data and algorithms. This ensures optimal treatment choices for patients.
- Conduct large-scale studies: EHRs provide researchers with access to extensive de-identified data. This facilitates large-scale studies and robust research findings.
- Facilitate comparative effectiveness research: EHRs allow for the comparison of treatment outcomes and interventions. This informs the development of evidence-based guidelines and protocols.
More easily identify trends and patterns
EHRs equipped with data visualization and analytics capabilities help healthcare professionals identify emerging trends and patterns in patient health. This enables them to:
- Spot early warning signs: EHRs help spot early warning signs by analyzing data trends. Timely interventions lead to improved patient outcomes.
- Identify population health trends: EHRs identify population health trends like disease prevalence and medication adherence. This aids in developing targeted public health strategies.
Support evidence-based medicine
EHRs integrate clinical guidelines, best practices, and decision-support tools to help healthcare professionals in delivering evidence-based care. With EHRs, healthcare providers can:
- Access clinical decision support: EHRs provide real-time alerts based on clinical guidelines. This enhances care quality by offering evidence-based information.
- Promote adherence to protocols: EHRs enforce adherence to protocols through prompts and reminders. This standardizes practices and improves consistency in care delivery.
Population health management
EHRs facilitate the monitoring and management of population health by providing tools for tracking health outcomes, identifying at-risk populations, and implementing targeted interventions. With EHRs, healthcare providers can:
- Identify and manage chronic conditions: EHRs aid in tracking chronic conditions for effective management. This enables proactive interventions and personalized care plans.
- Monitor population-level health indicators: EHRs analyze population-level data to monitor key health indicators. This informs public health interventions and evaluates program impact.
Eliminate legibility errors
One significant advantage of EHRs is that they eliminate the risk of misinterpretation or errors due to poor handwriting. Healthcare providers will:
- Improve accuracy and comprehension: EHRs offer legible documentation, reducing errors. This enhances patient safety and communication among professionals.
- Enhance coding accuracy: EHRs use standardized coding systems, minimizing errors. This leads to more accurate data handling.
Reduce medication errors
EHRs include built-in features such as medication reconciliation and automated drug interaction alerts. These functionalities help reduce the risk of medication errors and adverse drug events by:
- Enhancing medication safety: EHRs offer immediate access to complete medication lists. Alerts within the system prevent errors and ensure safe prescribing.
- Supporting clinical decision support for medications: EHRs integrate tools for medication selection and interaction checks. This aids providers in making informed prescribing decisions.
Provides physicians access to the most current information
EHRs provide physicians with instant access to the most up-to-date medical knowledge and guidelines. This enables them to:
- Stay informed: EHRs include medical knowledge resources like clinical guidelines. This ensures up-to-date information for better patient care.
- Enhance interdisciplinary collaboration: EHRs enable information sharing among healthcare providers. This improves communication and care coordination.
By leveraging the benefits of EHRs in clinical decision making, healthcare professionals can make informed choices, deliver evidence-based care, reduce errors, and improve population health outcomes.
Privacy and security
Ensuring the privacy and security of patient information is of utmost importance in Electronic Health Records (EHRs) systems. Healthcare providers and organizations implement robust measures to safeguard sensitive data and protect patient confidentiality. Let's explore the key aspects of privacy and security associated with EHRs:
Confidentiality
EHRs use strict protocols and access controls to protect patient data. Only authorized users can access this information, ensuring confidentiality.
Access controls
EHRs employ Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to limit data access to authorized personnel. This maintains data integrity and minimizes unauthorized disclosure risks.
HIPAA
EHRs comply with HIPAA regulations, safeguarding patient privacy through encryption, secure protocols, and staff training. This ensures both confidentiality and regulatory compliance.
Encryption
EHRs use strong encryption to secure patient data during transmission and storage. This makes intercepted data unreadable without an authorized key.
Audit Trails
EHRs maintain audit trails that log data-related activities. These trails are crucial for monitoring usage, detecting unauthorized access, and ensuring system integrity.
By implementing stringent privacy and security measures, EHR systems ensure the confidentiality of patient information, protect against unauthorized access, and comply with regulatory standards. These measures instill patient trust in the security of their personal health information.
Challenges associated with implementing EHRs
Implementing EHRs offers benefits but also presents challenges. A 2020 review of 26 studies identified common barriers like privacy concerns, costs, workflow disruptions, and system complexity. Despite these persistent issues, new solutions and strategies are available for effective implementation.
Let's look at the common challenges associated with implementing EHRs and strategies to overcome them:
Patient access to records
Enabling patients to access their health records empowers them to take an active role in their care. It promotes transparency and allows for informed decision making. Challenges in this area include:
- Privacy concerns: Secure patient portals and education on privacy rights address the balance between access and privacy.
- Health literacy and technological barriers: User-friendly portals and educational support overcome literacy and tech barriers for patient access.
Interoperability
Interoperability enables smooth information exchange between healthcare systems and providers. Its absence can limit EHR effectiveness and pose challenges.
- Data standardization: Standardized data models like HL7 and SNOMED CT solve format inconsistencies and promote interoperability.
- Integration with external systems: Using industry-standard protocols like FHIR ensures smooth data exchange with external systems.
- Lack of universal connectivity: Collaboration and investment in network infrastructure address technological gaps and enhance interoperability.
User experience and usability
User experience and usability are essential factors that influence the acceptance and adoption of EHR systems by healthcare professionals. Challenges in this area include:
- Complexity and learning curve: EHR systems can have intricate interfaces and functionalities, making them overwhelming for users who are unfamiliar with the technology.
- Workflow disruptions: Poorly designed EHR systems can disrupt established clinical workflows, leading to reduced efficiency and frustration among healthcare professionals.
- Lack of customization: Every healthcare organization has unique needs and workflows. The lack of customization options in EHR systems can limit their adaptability to specific clinical practices.
Real-life example: EHR challenges can be mitigated with ongoing training
Dr. Azza El.Mahalli, a Professor of Public Health at Abdul Rahman Bin Faisal University, shared some insights into how the complexity of EHRs can be challenging for physicians.
She referenced how doctors can be used to handwritten notes and short summaries. This conditioning can often lead them to find it time-consuming and burdensome to type out patient records, notes, and prescriptions digitally for EHRs.
Because of this difficulty, physicians may need a significant amount of additional time to complete this data entry process. This can sometimes even interrupt their consultations with patients.
Imagine a doctor having to stop in the middle of discussing a patient's health to deal with typing in information. This interruption breaks the natural flow of care and attention they want to give to their patients.
Dr. Mahalli's insight sheds light on a common problem experienced by many physicians. It's not just about the time it takes to type the data; it's about how this task affects the quality of care doctors aim to provide.
Providing comprehensive training, intuitive user interfaces, and ongoing support can mitigate the challenges associated with the learning curve
As mentioned above, having to input data into various fields on an EHR platform can interrupt a consultation with a patient.
Engaging end-users in the design and customization of EHR workflows, conducting usability testing, and continuously refining the system based on feedback can optimize workflow integration leading to better care.
The ideal EHR system can be achieved by working with physicians to identify their individual systems and processes. A highly tailored process will reduce challenges for providers while improving patient experience.
Privacy and protection
Protecting patient data from breaches and cybersecurity threats is a critical concern when implementing EHR systems. Challenges here are:
- Data breaches: Robust security measures like encryption and firewalls protect against unauthorized access and breaches.
- Cybersecurity threats: Regular assessments and staff education minimize evolving cybersecurity risks.
- Compliance with privacy regulations: Privacy policies, staff training, and audits ensure adherence to regulations like HIPAA.
Data integrity and accuracy
Ensuring data integrity and accuracy is vital for the effective use of EHRs. Challenges in this area include:
- Data entry errors: User-friendly interfaces and data validation techniques minimize entry mistakes.
- Incomplete or inconsistent documentation: Standardized templates and regular audits ensure data completeness and consistency.
- Data migration and conversion: Proper data cleansing and validation are crucial for a smooth transition to EHRs.
Provider patient engagement
Effective provider and patient engagement is essential for maximizing the benefits of EHR systems. Challenges in this realm include:
- Limited patient involvement: Educating patients and facilitating digital communication enhance patient engagement with EHRs.
By addressing these challenges with appropriate strategies and solutions, healthcare organizations can overcome implementation obstacles and maximize the benefits of EHR systems.
Quick tips: How to Implement Electronic Health Records (EHRs) in Your Practice
mplementing an Electronic Health Records (EHR) system can be a complex but rewarding endeavor. Here are actionable steps to guide you through the process:
Step 1: Conduct a Needs Assessment
- Evaluate the specific needs of your healthcare practice.
- Identify the problems that an EHR system can solve, such as inefficiencies in patient record-keeping or billing.
Step 2: Assemble a Project Team
- Include representatives from various departments like IT, administration, and clinical staff.
- This team will be responsible for overseeing the implementation process.
Step 3: Choose the Right EHR Vendor
- Research and compare different EHR vendors based on features, customer reviews, and compliance with standards like HIPAA.
- Consider opting for a vendor that offers a customizable solution to meet your practice's unique needs.
Step 4: Budget and Financing
- Determine the budget for implementing and maintaining the EHR system.
- Explore financing options, including grants and loans, to offset the initial costs.
Step 5: Data Migration
- Plan how you will migrate existing patient records into the new EHR system.
- Ensure that data cleansing and validation are part of this process to maintain data integrity.
Step 6: Staff Training
- Conduct comprehensive training sessions for all users to familiarize them with the new system.
- Offer ongoing support and additional training as needed.
Step 7: Pilot Testing
- Start with a small-scale implementation to test the system’s functionality and to identify any issues.
- Use feedback from this phase to make necessary adjustments.
Step 8: Full-Scale Implementation
- Once pilot testing is successful, proceed with full-scale implementation.
- Monitor the system closely during the initial weeks to address any issues promptly.
Step 9: Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
- Regularly update the EHR software to benefit from new features and security enhancements.
- Continuously monitor system performance and user feedback to make ongoing improvements.
Step 10: Measure ROI and Impact
- After a set period, evaluate the impact of the EHR system on operational efficiency and patient care.
- Use key performance indicators (KPIs) like time saved, error rates, and patient satisfaction scores to measure ROI.
By following these steps, you can successfully implement an EHR system that not only meets regulatory requirements but also brings about significant improvements in patient care and operational efficiency.
Leveraging EHR to improve all-around patient care
Electronic health records (EHRs) have revolutionized healthcare by enhancing patient care, streamlining operations, and facilitating informed decision-making. While EHRs offer numerous benefits, they also present challenges that require strategic solutions. By proactively addressing these issues, healthcare organizations can unlock the full potential of EHR systems, leading to improved patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, EHRs will remain pivotal in shaping its future. To stay updated on the latest trends, best practices, and solutions related to EHRs, subscribe to The Medical Practice newsletter.



