Mastering the revenue cycle is essential for medical offices; success hinges on understanding the entire process from patient registration to collections.
An efficient medical billing workflow enhances cash flow and patient satisfaction while minimizing claims denials and payment delays—key for sustained practice growth.
Partnering with expert medical billing services can reduce errors, speed up payments, and improve overall financial health for practices.
Managing the revenue cycle in a medical office isn’t just about sending out claims and hoping they get paid. It's a complex, multi-step process that requires coordination, accuracy, and persistence. I’ve spent years fine-tuning this process, and I know firsthand how much smoother things run when everyone on the team understands how it all fits together.
This guide breaks down what medical billing really involves, why it matters, and the step-by-step flow that keeps the lights on in your practice.
What is the Medical Billing Workflow?
The medical billing workflow is the mechanism by which we translate healthcare services into billing claims, then submitting them to insurance companies or patients for reimbursement. It connects the clinical and administrative sides of a practice. On one end, the provider delivers care; on the other, the biller ensures the practice gets paid for it.
Importance of an Efficient Medical Billing Workflow
A well-run billing operation isn’t just about revenue—it’s about sustainability. I've seen practices with top-tier providers struggle to stay afloat simply because of billing inefficiencies. Denied claims, slow payments, and inaccurate coding all eat into cash flow.
Efficiency here means:
- fewer payment delays
- less rework
- better communication between front office, providers, and billing staff
- improved patient satisfaction
For me, optimizing the billing process isn't just good practice—it's good business.
My Medical Billing Flowchart (steal this!)
Here’s a high-level flowchart to visualize how everything connects. This overview has helped me train new hires and spot bottlenecks in the system.
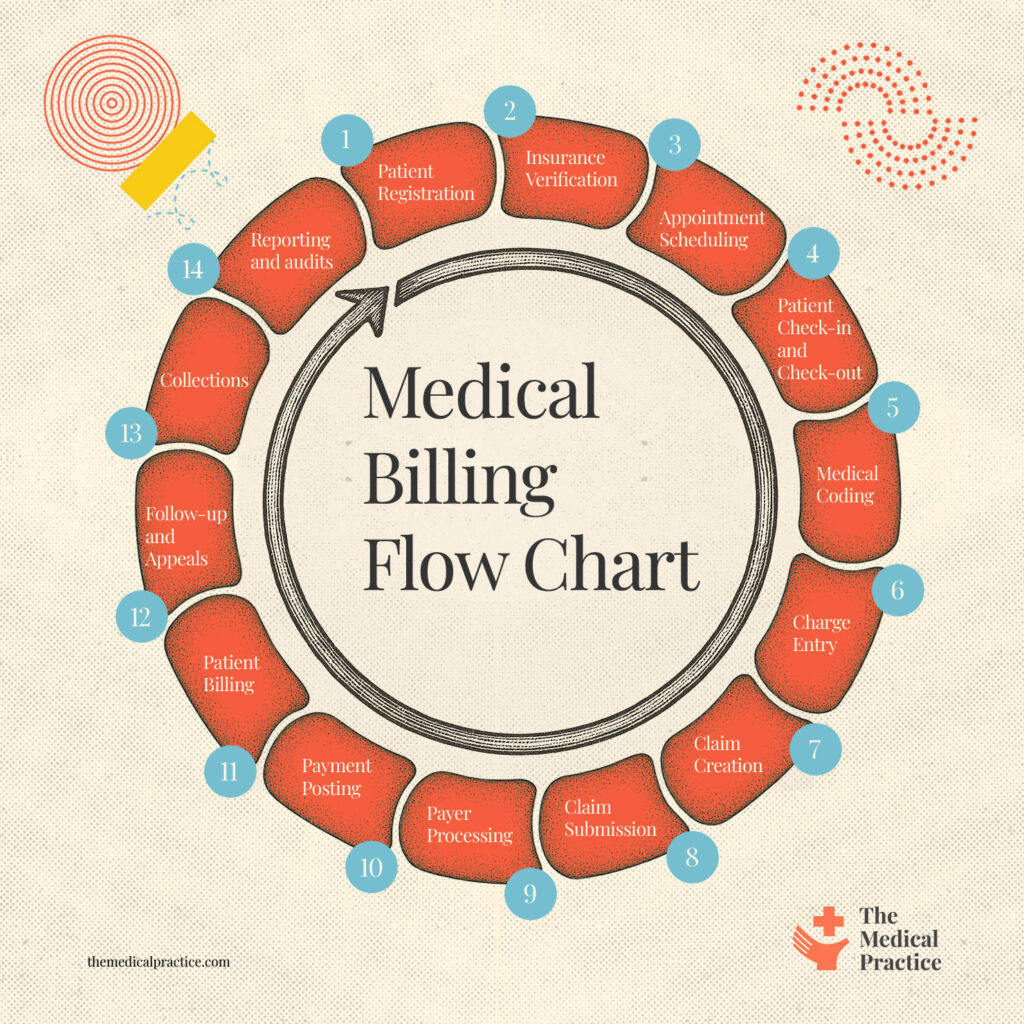
Medical Billing Workflow Explained
Let’s walk through each step in the process. In my practice, every one of these steps has an owner and a set of checks to avoid errors and delays.
1. Patient Registration
This is where it all starts. Get accurate demographics and insurance info upfront. Train front desk staff to double-check names, policy numbers, and plan details—mistakes here will ripple down the entire chain.
2. Insurance Verification
Before the visit, confirm eligibility and benefits. I always say: no verification, no visit. If coverage is inactive or the service isn’t covered, that needs to be addressed before care is delivered.
3. Appointment Scheduling
Make sure your scheduling system captures visit type and any pre-authorization requirements. Good notes here help with coding and reduce denials later.
4. Patient Check-in and Check-out
At check-in, reconfirm insurance and collect any copays. At check-out, make sure documentation is complete and any follow-ups are scheduled. This is also a good time to collect balances or set up payment plans.
5. Medical Coding
Coders translate provider documentation into CPT, ICD-10, and HCPCS codes. Accuracy is crucial—upcoding or undercoding can lead to audits or lost revenue. Make sure your providers document thoroughly and that coders are well-trained.
Be sure to record z codes, if you use those, or NOC codes, if you are in the USA.
6. Charge Entry
Charge entry turns codes into billable charges. This usually happens in your EHR or practice management software. We’ve implemented a “second eyes” process to catch any discrepancies before claims go out.
7. Claim Creation
The billing software compiles charges, codes, and patient info into a standardized claim format (usually ANSI 837P). Claims should be scrubbed for errors before submission.
8. Claim Submission
Claims go out electronically to payers via clearinghouses. Set up daily submissions and track rejections in real-time. The sooner they go out, the sooner you get paid.
9. Payer Processing
This is out of your hands, but you can monitor progress through remittance advice reports. Insurance companies may accept, deny, or partially pay a claim.
10. Payment Posting
Once payments arrive (either electronically or by check), they need to be posted accurately against the correct accounts. This is where you reconcile the explanation of benefits (EOBs) with your charges.
11. Patient Billing
After insurance has paid their portion, remaining balances are billed to the patient. Clear statements, online portals, and flexible payment options all improve collections.
12. Follow-up and Appeals
Denied or underpaid claims need timely follow-up. You should have dedicated staff for appeals who know each payer’s policies and timelines. Don’t let claims age out.
13. Collections
When patient balances go unpaid, they move to collections. We give patients at least three notices before involving a collections agency, and we always offer payment plans first.
14. Reporting and Audits
Finally, keep an eye on the numbers. Monitor days in A/R, denial rates, and clean claim rates. Regular audits catch trends before they become revenue leaks. This is how you turn billing into a performance engine, not just a back-office task.
Outsourcing the Medical Billing Process
Partnering with professional medical billing services means that critical administrative tasks like submitting claims, managing patient statements, processing patient payments, and maintaining accurate patient records are handled by trained experts.
Outsourcing also supports long-term financial health by reducing errors and speeding up reimbursements. Tasks like credentialing, which are essential but time-consuming, are often more effectively managed by third-party billing teams.
Here are my suggestions for medical billing services you can rely on:
Medical Billing Process FAQs
Here are some additional questions people also ask me about the medical billing process.io
What is revenue cycle management, and how does it affect medical billing?
Healthcare revenue cycle management (RCM) is the backbone of the medical billing process. It encompasses every step from patient registration to final payment collection. Key tasks include: verifying financial responsibility, managing accounts receivable, and processing claims efficiently to avoid claim denials. A well-structured RCM system helps streamline the billing workflow by ensuring timely submission of claims and effective denial management.ns
How does insurance eligibility verification impact the billing cycle?
In the medical billing process, insurance eligibility verification is a crucial first step. Confirming a patient’s insurance coverage, insurance information, and identifying the insurance provider helps prevent costly errors and claim denials.
When a patient’s insurance eligibility is verified early, billers can submit accurate claims to medicare or private payers. This reduces delays in adjudication and improves reimbursement speed. f
How does automation and electronic health records improve the billing process?
The integration of automated systems and electronic health records (EHRs) has revolutionized medical billing. Automation reduces manual errors in coding, claims processing, and data entry, improving speed and accuracy.
EHRs store critical patient information, helping billers access everything needed for claim submission in one place. These technologies enable real-time eligibility checks, accelerate billing cycles, and support a more efficient revenue cycle management process overall.
What is assignment of benefits (AOB) in medical billing?
Assignment of benefits (AOB) in medical billing is when a patient allows their healthcare provider to receive insurance payments directly from the insurer. This simplifies the billing process but can shift financial responsibility to the patient if claims are denied.
Need help selecting the right software for your medical practice?
We’ve joined up with Crozdesk.com to give all our readers (yes, you!) access to Crozdesk’s software advisors. Just use the form below to share your needs, and they will contact you at no cost or commitment. You will then be matched and connected to a shortlist of vendors that best fit your company, and you can access exclusive software discounts!
What Next?
To stay updated on the latest trends, best practices, and solutions related to your medical practice, subscribe to The Medical Practice newsletter.




