AI technologies enhance patient outcomes and support clinical decisions, making healthcare more efficient and effective for both providers and patients.
As AI integrates into healthcare, ethical considerations such as privacy and trust must be prioritized to maintain patient confidence and care quality.
Emerging trends forecast significant advancements in AI, promising increased adoption and innovative applications in healthcare by the year 2025.
Practical solutions and real-world experiences highlight how healthcare professionals can successfully implement AI while ensuring patient care remains a top priority.
What is the future of AI in healthcare? In this article, I’ll share the latest 2025 trends, ethical considerations, and practical solutions drawn from real-world experience. You’ll walk away with actionable insights to help you harness AI’s full potential while protecting what matters most: patient trust and care quality.
What is AI in Healthcare?
AI in healthcare refers to the use of artificial intelligence technologies, like machine learning and natural language processing, to analyze complex medical data. It helps improve patient outcomes, streamline operations, and support clinical decision-making.
How Is AI Being Used in Healthcare?
AI is already being used in healthcare, and has been for some time. Common uses of AI in healthcare include:
- Diagnosing diseases from imaging and lab results
- Predicting patient risk and hospital readmissions
- Automating administrative tasks like prior authorizations
- Enhancing medical billing and coding accuracy
- Supporting clinical decisions through evidence-based recommendations
- Managing population health through predictive analytics
- Personalizing treatment plans using genomic data
Generative AI in Healthcare
Many people confuse “artificial intelligence” with “generative AI” tools like ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini. AI as a buzzword has blown-up ever since ChatGPT went mainstream. Some people are wondering if learning language models (LLMs) have a practical use in a healthcare environment.
So far, we are seeing that it is able to enhance diagnostics, personalize treatment, and improve patient engagement. Here’s how it’s being used across various domains:
1. Clinical Applications
Generative AI enhances decision-making, speeds up documentation, and supports personalized treatment by generating insights from vast medical data sources. Let's look at some examples of how AI is being used in diagnostics and discovery.
Predictive & Preventive Care
It is far cheaper and more empathetic to catch health issues before they become life-alterring to our patients. Here is how we can leverage genAI to do so:
- genAI can synthesize EHR data to predict disease progression (e.g., onset of diabetes, risk of stroke).
- genAI can simulate patient trajectories, helping clinicians intervene earlier with preventive measures.
Diagnostic Assistance
Generative AI can analyze complex medical data to generate accurate, timely differential diagnoses, helping clinicians detect conditions earlier and reduce diagnostic errors. Here are some examples:
- Radiology: genAI models like generative adversarial networks (GANs) enhance medical imaging resolution and help identify anomalies (e.g., tumors, fractures) in X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans.
- Pathology: AI models generate synthetic pathology slides for training or augment limited datasets, improving cancer detection.
Drug Discovery & Development
Generative AI accelerates drug discovery and development by simulating molecular interactions, generating novel compounds, and predicting drug efficacy and safety, significantly reducing time and costs in the R&D process. For example:
- Molecule Generation: genAI tools design novel drug candidates by predicting molecular structures with desired properties. This can streamline the early stages of drug discovery and accelerate the identification of viable therapeutic compounds.
- Simulation: genAI tools can generate virtual clinical trial data to simulate outcomes and reduce the need for lengthy early-stage trials.
2. Operational Efficiency
Running a medical practice is hard work, but genAI tools can help automate day-to-day tasks. Generative AI can optimize scheduling and streamlining workflows, allowing providers to focus more on patient care and reduce system-wide cost. Here are some key examples:
Medical Documentation
Generative AI can automatically generate accurate, context-aware clinical notes and summaries, reducing clinician workload and enhancing the quality and consistency of patient records. For example:
- Clinical Note Generation: genAI automatically generates SOAP notes or discharge summaries from doctor-patient conversations, reducing administrative burden.
- Coding Assistance: genAI helps medical coders assign accurate billing codes by analyzing and summarizing medical records.
Scheduling & Workflow Automation
Many tools you already use have AI built-in, providing context-aware reports and predictive analytics that help you make workload and resource management decisions.
- Scheduling Automation: genAI helps optimize appointment booking by predicting patient no-shows, managing overbookings, and aligning provider availability with patient demand.
- Workflow Automation: genAI helps streamline repetitive tasks like intake processing, documentation, and follow-ups, enabling staff to focus on high-value care activities and reducing administrative bottlenecks.
3. Patient-Facing Applications
We are facing large-scale healthcare personnel shortages almost everywhere right now. GenAI can help bridge that gap in a few ways:
Virtual Health Assistants
Generative AI powers virtual health assistants to deliver personalized, real-time support for patients by answering medical queries and managing appointments. For example:
- Healthcare Chatbots: genAI powers empathetic, conversational agents that answer patient queries, provide medication reminders, and offer health advice based on individual data.
Personalized Health Education
Generative AI can deliver tailored, easy-to-understand information based on individual patient profiles, improving engagement and adherence to care plans. Like:
- Deep Personalization: genAI can generate tailored health content (e.g., dietary plans, post-op instructions) based on a patient’s condition, preferences, and literacy level.
4. Research & Training
And, of course, one of my favorite spaces to explore the potential of genAI enhancement:
- Synthetic Data Generation: genAI produces synthetic patient data that mimics real-world data without privacy risks, useful for research and model training.
- Education: AI tutors simulate clinical cases for medical student training or continuing education.
Risks of AI in Healthcare
Every new technology comes with associated risks. When talking about AI in healthcare, here are some considerations I am keeping my eye on:
- Inaccurate or biased data leading to misdiagnosis
- Lack of transparency in AI decision-making (black-box models)
- Data privacy and security concerns
- Over-reliance on AI over clinical judgment
- Displacement of certain healthcare roles
Ethical Consideration of AI in Healthcare
The ethical landscape of AI in healthcare is still evolving, and it's something I take seriously as a practice manager. One major concern is patient consent. Many patients don't fully understand how their data might be used or shared by AI systems. Transparency is critical, especially when AI is used to guide or influence treatment decisions.
Another area is bias. AI systems are only as good as the data they're trained on. If that data is skewed or incomplete, it can worsen healthcare disparities rather than reduce them. We need strict oversight and clear accountability when AI is integrated into patient care workflows.
Finally, there's the issue of trust. Patients need to feel confident that AI isn't replacing their providers, but rather supporting them. It’s our responsibility to ensure AI serves the human side of medicine, not the other way around.
What Are the Benefits of Using AI in Healthcare?
AI brings clear, measurable improvements to both patient care and medical operations. It can help us move faster, make data-driven decisions, and streamline repetitive tasks that bog us down:
- Faster diagnosis: AI tools can quickly scan medical images and flag abnormalities in minutes.
- Improved accuracy: Algorithms can catch patterns and details that human eyes might miss.
- Administrative efficiency: AI automates repetitive tasks like documentation and coding.
- Predictive analytics: AI can help forecast disease progression or readmission risks.
- Cost savings: By reducing errors and increasing efficiency, AI helps cut down healthcare costs.
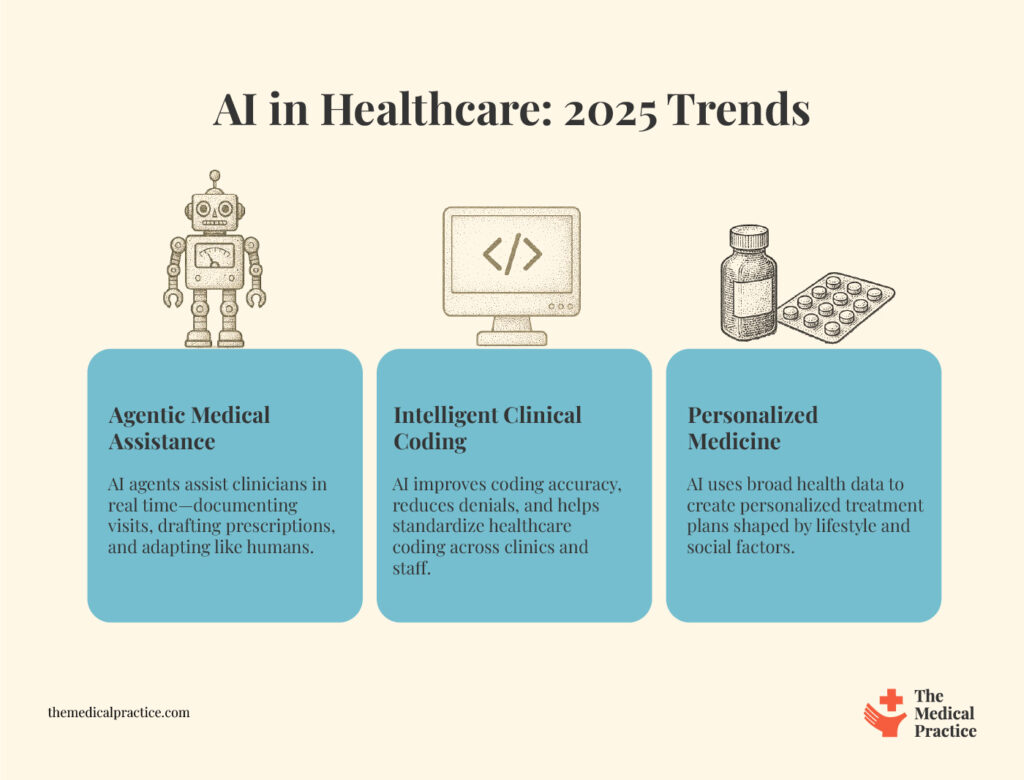
Top 3 Trends of AI in Healthcare for 2025
Here are some exciting trends I’m seeing around AI in healthcare right now.
1. Agentic medical assistance
AI agents are evolving to support clinicians in real time. These systems can listen, analyze, and respond during patient visits, helping document the encounter, suggest next steps, and even draft prescriptions.
Amanda Saunders, director of generative AI software marketing at NVIDIA, notes that: “Agentic AI builds on generative AI, taking simple responses further with the ability to consider options, go back and redo steps. It works much more like we do when we solve problems and work out how to consider new information.”
And it’s not just physician assistance I’m seeing. With staffing shortages across the board, AI is stepping in to handle everything from triage chatbots to transcription. It helps us maintain service levels without burning out the team.
2. Intelligent clinical coding
We're seeing smarter AI tools that can code procedures and diagnoses from notes with very high accuracy. This is cutting down on denials and speeding up revenue cycles in our practice.
There is also a huge problem with variance of coding techniques between clinics and, more importantly, between healthcare coding personnel (per British Journal of General Practice, 2024). Leveraging AI could help standardize coding practices in any given area or practice specialty.
3. Personalized medicine
AI is now able to process genetic, lifestyle, and historical health data to suggest treatments tailored to individual patients. After all, behavioral and social determinants (or other such external factors) account for about 60% of our health outcomes (whereas our genes account for only 30%, and actual medical history accounts for 10%).
Health data exists everywhere, from physicians’ notes to wearable lifestyle devices and even grocery and food purchase history reports. There is a future world where generative AI taps into healthcare “big data” across platforms to craft a truly unique wellness plan to suit different lifestyle qualities.
What's Next?
To stay updated on the latest trends, best practices, and solutions related to your medical practice, subscribe to The Medical Practice newsletter.